The Ultimate Guide for Businesses in the Global Economy
In 2025, as companies are increasingly tapping into the global talent pool offshore teams will no longer be something new. They’re becoming a competitive advantage. But with this expansion is a grim reality the number of data security incidents is increasing at a similar rate. According to IBM’s report 2024 that the cost of a breach was $4.45 million, which underscores the importance of having robust offshore team security protocols for data security.
Offshoring can bring cost savings in scalability, efficiency, and 24-hour operations but only in the context of the foundation of trust and compliance. It’s also a good idea to implement proactive strategies for protecting data. This guide provides specific, practical steps for companies to collaborate with confidence and safety offshore teams.
In 2025, as businesses increasingly tap into global talent pools, offshore teams are no longer a novelty—they’re a competitive advantage. Yet with this growth comes a sobering reality: data security incidents are rising just as fast. According to IBM’s 2024 report, the average cost of a data breach hit $4.45 million, underscoring the critical need for robust offshore team data security protocols.
Offshoring can unlock cost efficiencies, scalability, and 24/7 operations, but only if it’s built on a foundation of trust, compliance, and proactive data protection strategies. This guide offers clear, actionable steps to help companies collaborate safely and confidently with offshore teams.
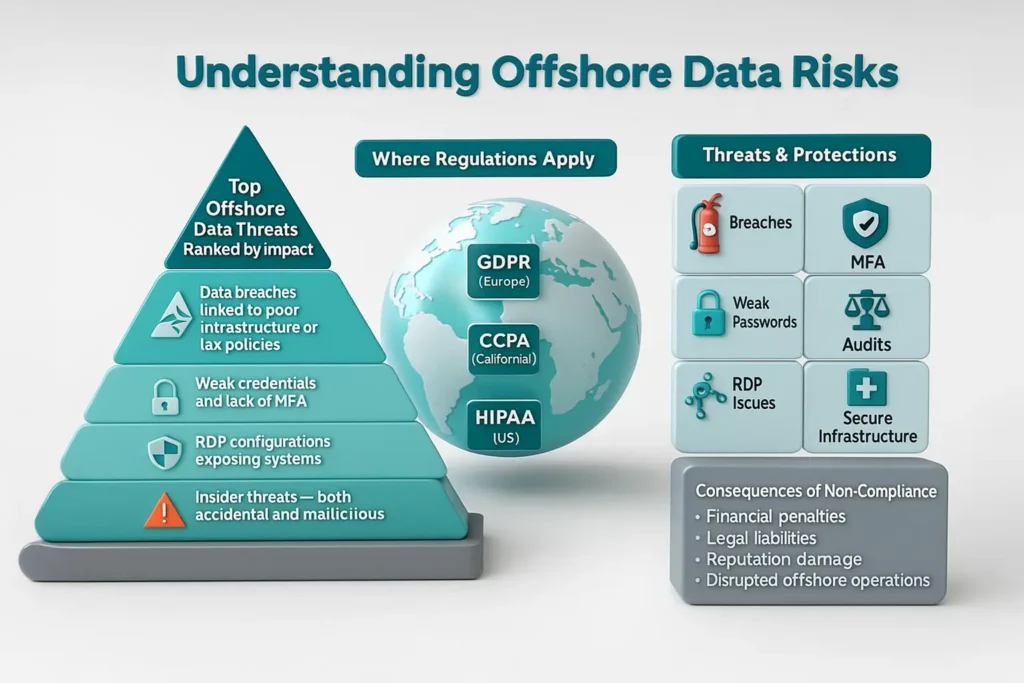
Before diving into solutions, it’s important to recognize the unique risks that come with offshore data processing and remote collaboration.
Cross-border data handling introduces legal complexities. Companies must comply with data protection laws such as:
Failing to align your offshore IT support with these standards can expose you to legal and financial penalties.
Not all vendors are created equal. Choosing the right offshore partner is the first step toward long-term data security outsourcing success.
This level of scrutiny is vital whether you’re outsourcing development, offshore cloud services, or contact center operations.
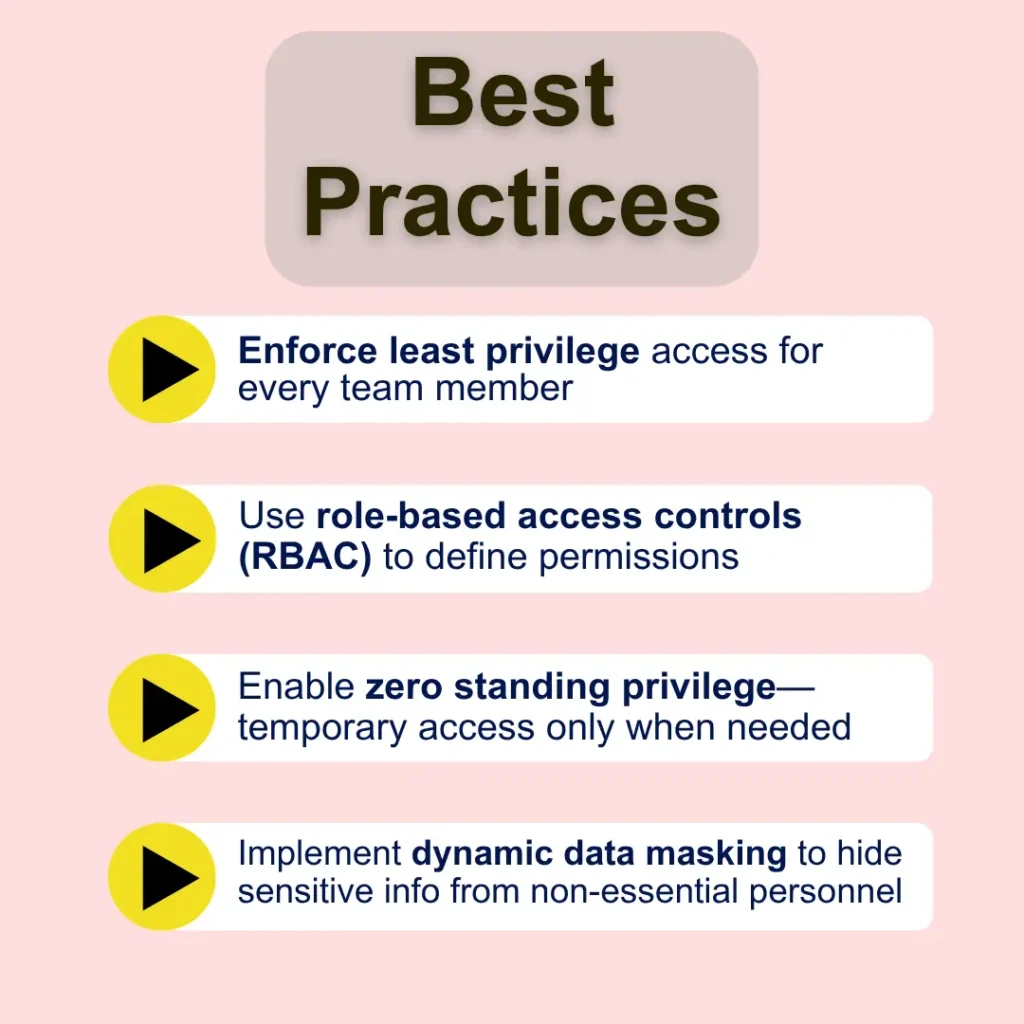
One of the most effective strategies for offshore data protection is limiting access from the start.
For DevOps, IT admins, and infrastructure roles, these principles are non-negotiable.
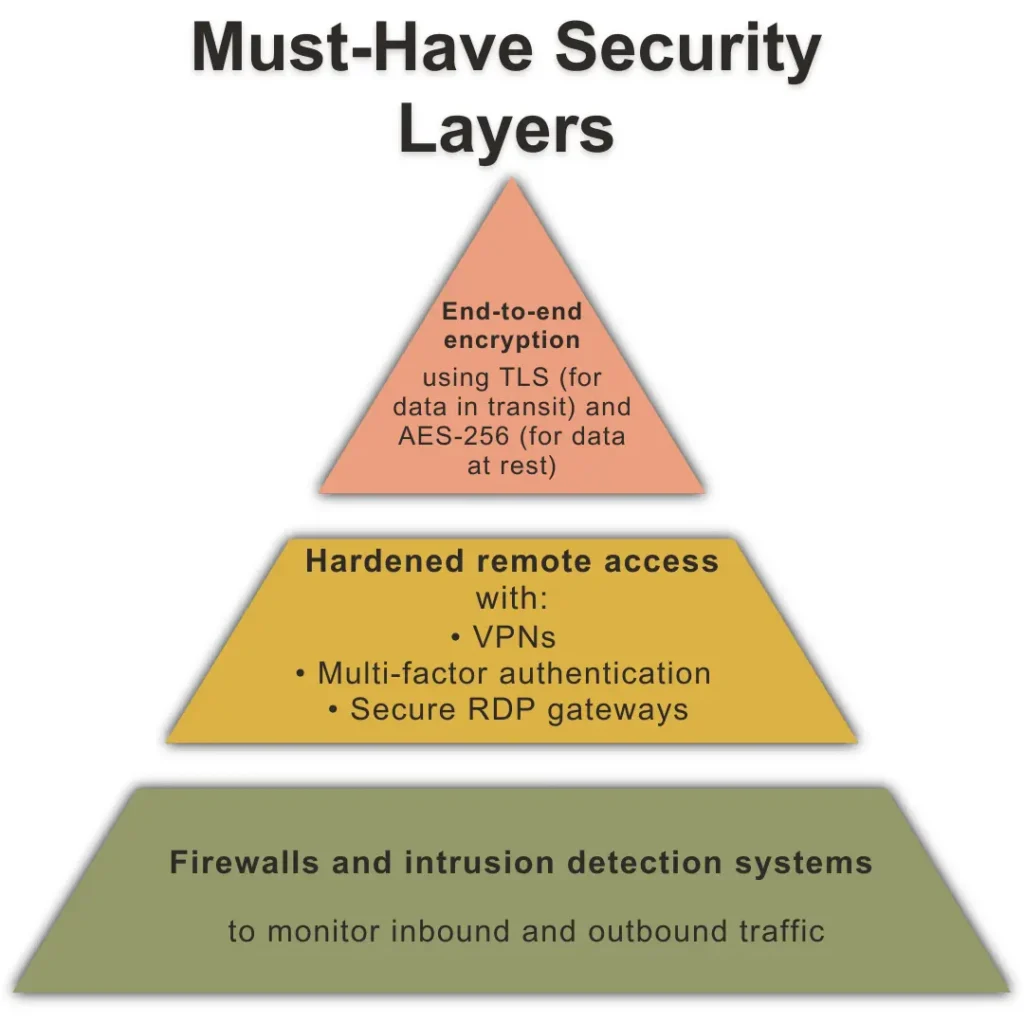
The security of your offshore setup is only as strong as its weakest point. Strengthen every layer of your technology stack.
Whether your team is managing offshore cloud infrastructure or sensitive internal applications, hardening your environment is crucial.
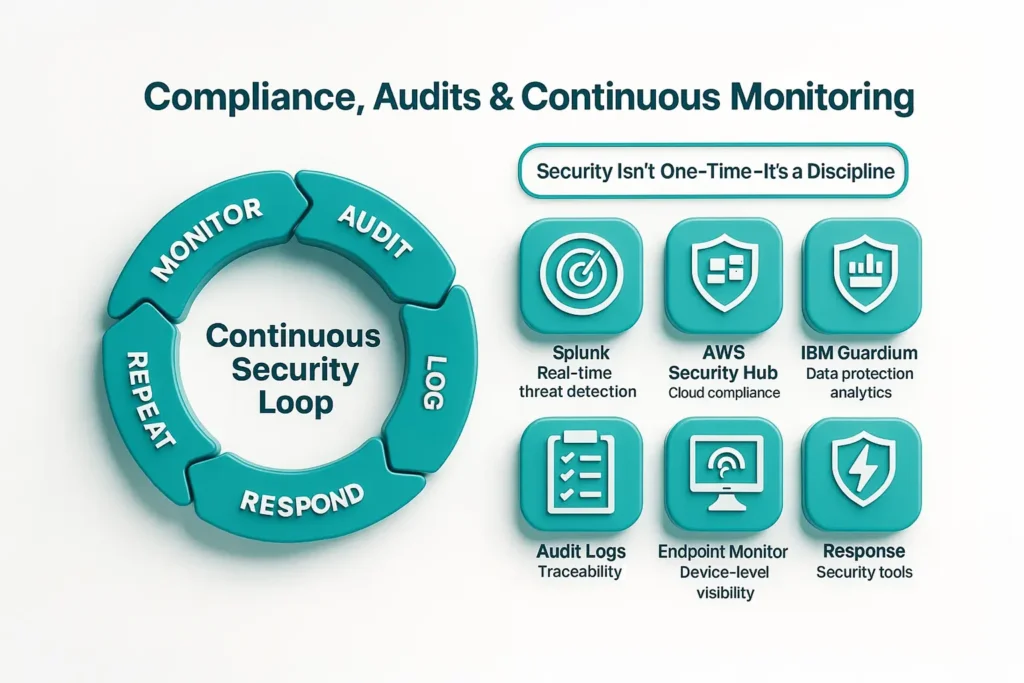
Security isn’t a one-time event—it’s a continuous process.
Tips: Continuous monitoring ensures accountability and rapid response in case of anomalies.

Even with the best defenses, incidents can happen. A well-documented incident response plan can make or break your recovery efforts.
For regulated industries like finance and healthcare, this plan is essential.
Your offshore team’s security awareness is just as important as their technical skills.
Security should be part of your offshore team’s onboarding and continuous development, not an afterthought.
Visibility is the backbone of trust when managing offshore data services.
These tools help maintain compliance, especially in industries requiring strict data controls like healthcare, banking, and SaaS.
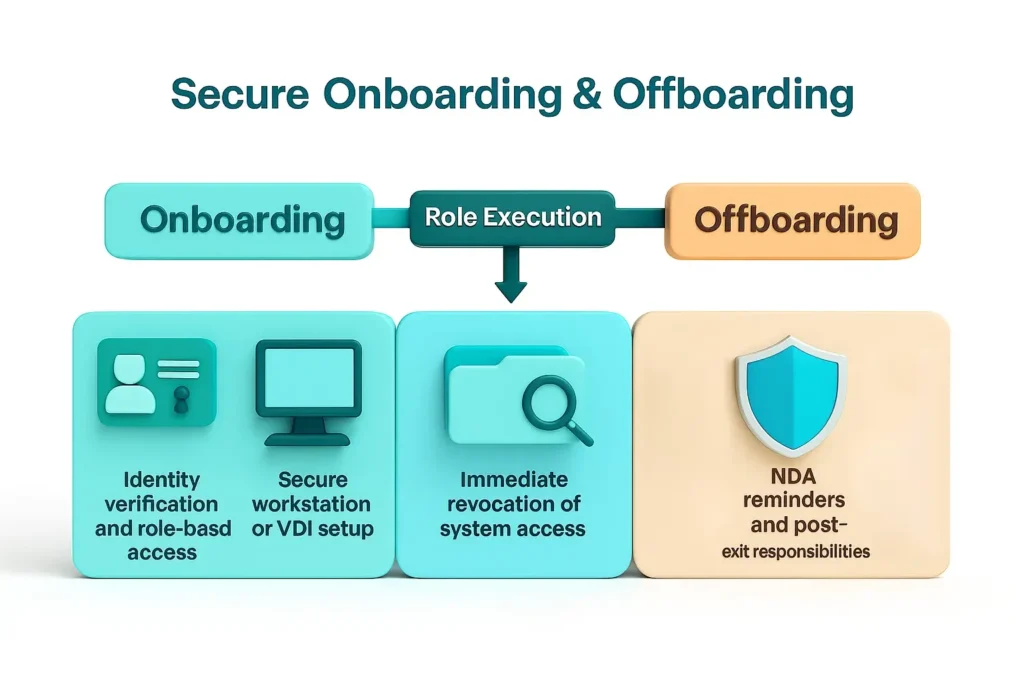
Mistakes often happen during access transitions. A secure process ensures consistency and protection.
This reduces risk, particularly for roles with access to sensitive offshore data environments.

These examples show that offshore team data security isn’t just theory—it’s achievable.
Working with offshore teams doesn’t mean compromising data security. In fact, with the right strategy, it can enhance your company’s agility without increasing risk.
To recap:
In today’s interconnected world, data security outsourcing is a necessity—but doing it right gives you a global edge. Build your offshore support model on security, and you’ll scale smarter, not just faster.
To ensure data security in a cloud environment, you should always choose a cloud provider that uses robust encryption protocols, both at rest( when stored) and in transit (during transfer).
The two main methods used to ensure data security are authentication and authorization, which ensure that only authorized users can access enterprise data.
Five key steps that will help to ensure data security are: using strong authentication mechanisms, regular updating and patching systems, implementation of strong access control, encrypting data, and monitoring and auditing database activity.
The five protection methods for data security are: network security, encryption, data backups, access control, and physical security.
Implementation of robust access controls, strong data encryption, classification and identification of data, regular data backups and disaster recovery planning, awareness training and employee education, securing the physical infrastructure and storage devices, conducting security audity and monitoring user activities, patch management and software updates, adhering to relevant data protection laws and regulations and enforcing strong password protection.
The three types of cyber threats are Malware, Social Engineering, and Denial-of-Service (DoS) and Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDOS).
Encryption is the primary method that can be used to ensure data confidentiality because it encryption helps in transforming data into an unreadable format which indeed makes it inaccessible to unauthorized individuals.
Join thousands of businesses leveraging offshore staffing to scale their operations globally
Expand effortlessly with My Offshore Employees - access top 1% offshore talent starting at just $3/hr or $600/month per FTE. No hidden fees, no compromises on quality. Your offshore employees work exclusively for you - ensuring focus, transparency, and real-time visibility into your projects. We combine smart automation and proven industry experience to deliver higher productivity, fewer errors, and tailor-made solutions for your business growth.

© 2022-Present MyOffshoreEmployees.com – A brand of iWebGenics Pvt. Ltd. (India)