EdTech startups targeting the U.S. K–12 segment face a dual challenge: scaling curriculum development rapidly while ensuring adherence to academic standards. Accelerating course production without compromising pedagogical quality is particularly difficult for venture-backed startups under pressure to launch quickly.
According to a 2023 HolonIQ report, global EdTech investment surpassed $16 billion, yet 70% of startups cite content production bottlenecks as their primary growth inhibitor (HolonIQ, 2023). Offshore strategies are emerging as a solution, enabling companies to accelerate production cycles cost-effectively.
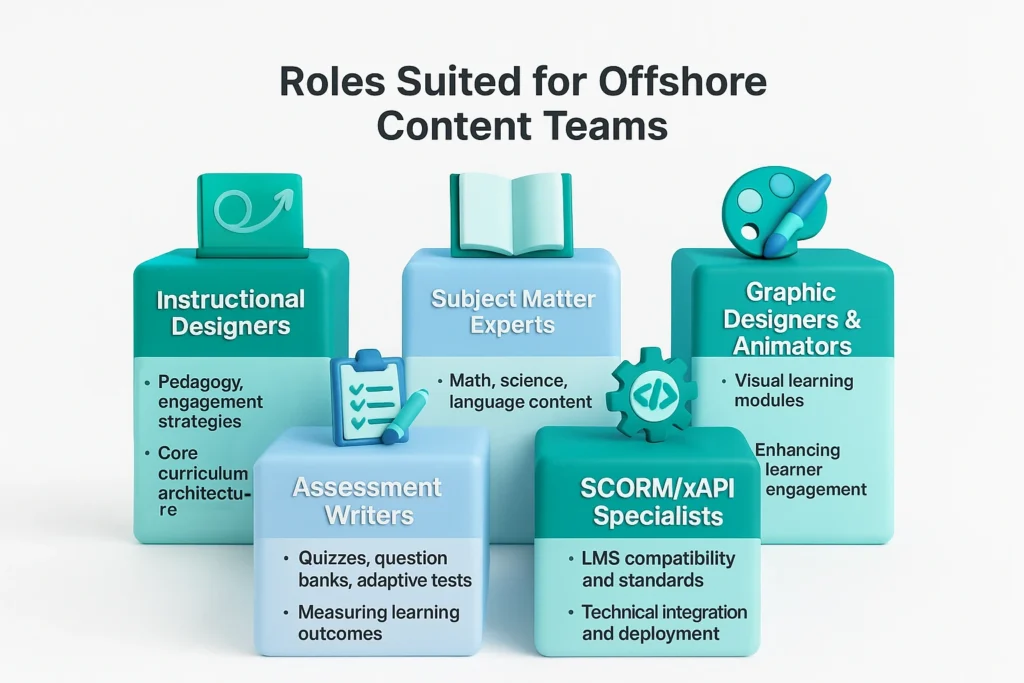
Not every role in EdTech can be outsourced, but process-driven tasks lend themselves well to offshore models. Common positions include:
These roles ensure a blend of educational rigor and engaging delivery, especially when global curriculum teams are structured with clear quality benchmarks.

A U.S.-based EdTech startup specializing in STEM content faced state-specific curriculum demands across six states. Instead of hiring 20+ in-house specialists, the company partnered with an instructional design offshore team in India. The results:
This approach allowed the startup to allocate capital toward LMS integrations and analytics, rather than ballooning internal payroll.

Collaboration is critical for distributed teams. Popular tools include:
Research highlights that using standardized authoring tools across global teams reduces revision cycles by 30%, improving overall speed-to-market (Kang et al., 2021).

Integrating content with Learning Management Systems (LMS) is often the final hurdle. Offshore teams specializing in LMS content development handle:
Advanced workflows combine content tagging, AI-based searchability, and analytics dashboards, ensuring real-time monitoring of learner engagement.
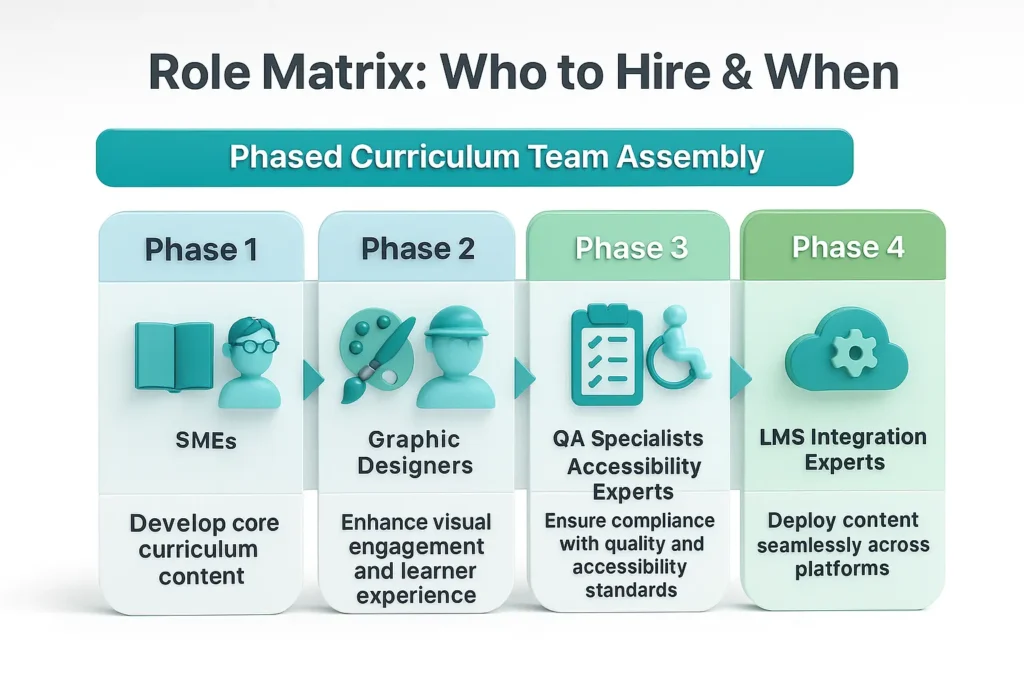
Building global curriculum teams requires a phased approach:
This sequencing ensures curriculum speed and quality remain balanced.
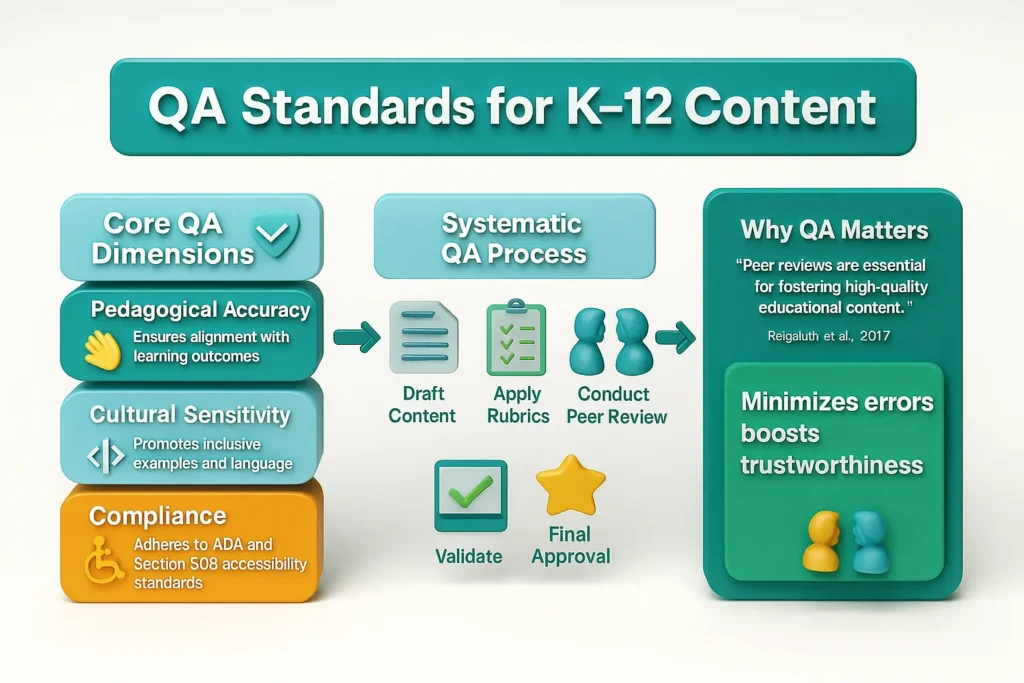
Quality assurance (QA) for K–12 learning materials includes:
A systematic QA process involving rubrics and peer reviews minimizes errors and enhances trustworthiness (Reigeluth et al., 2017).
For U.S. EdTech startups, the future of content operations lies in EdTech outsourcing models that blend instructional design offshore expertise with agile workflows. By leveraging global curriculum teams, startups can scale LMS content development without compromising quality—creating sustainable growth in a competitive market.
HolonIQ. (2023). Global Education Market Outlook: Investment Trends in EdTech.
https://www.holoniq.com/research/edtech-market-size-forecast/
Kang, M., Choi, H., & Kim, J. (2021). Distributed instructional design in global teams: Challenges and opportunities.
https://doi.org/10.1080/10494820.2021.1920509
Reigeluth, C. M., Beatty, B. J., & Myers, R. D. (2017). Instructional-Design Theories and Models: The Learner-Centered Paradigm of Education.
https://doi.org/10.4324/9781315707203
American Society for Training & Development (ASTD). (2020). Best Practices in LMS Implementation and QA Standards.
https://www.td.org/research-reports
World Bank. (2022). Digital Learning Readiness and EdTech Ecosystem Report.
https://www.worldbank.org/en/topic/education/publication/digital-learning-readiness
Join thousands of businesses leveraging offshore staffing to scale their operations globally
Expand effortlessly with My Offshore Employees - access top 1% offshore talent starting at just $3/hr or $600/month per FTE. No hidden fees, no compromises on quality. Your offshore employees work exclusively for you - ensuring focus, transparency, and real-time visibility into your projects. We combine smart automation and proven industry experience to deliver higher productivity, fewer errors, and tailor-made solutions for your business growth.
© 2025. All Rights Reserved.